Cellular Respiration In Plants Equation

Cellular respiration is a set of biochemical reactions that takes place in most cells.
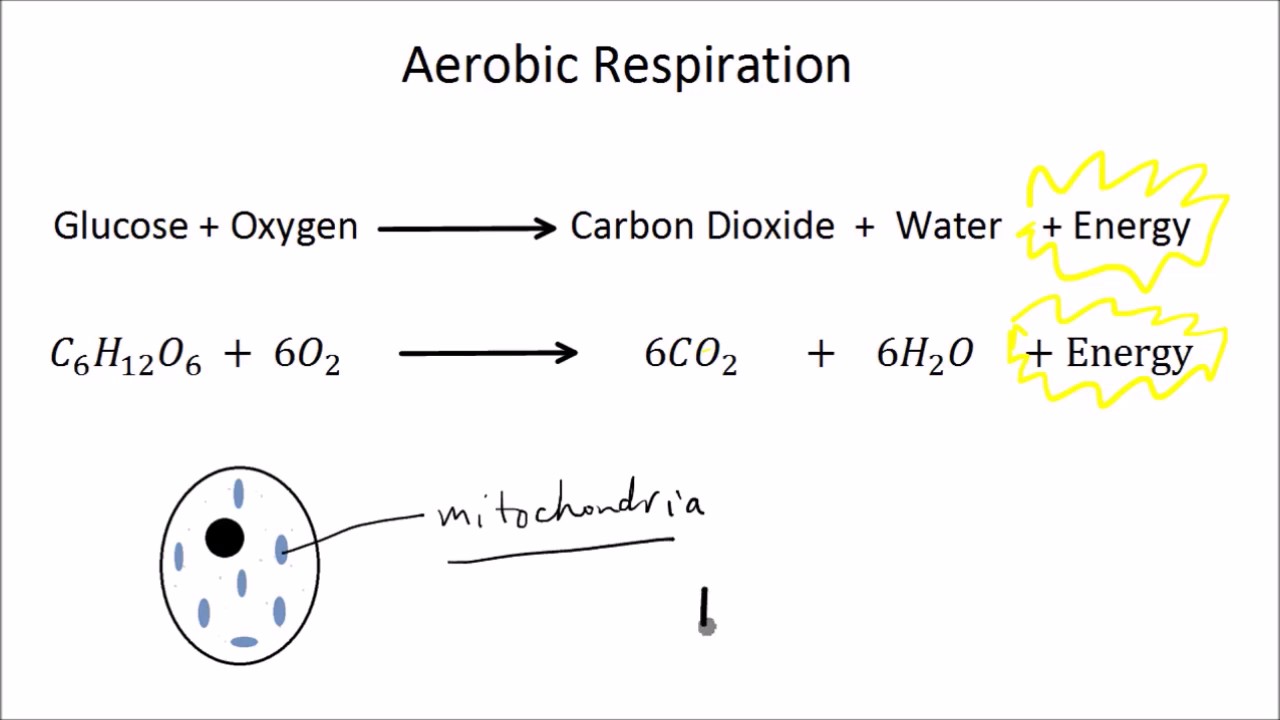
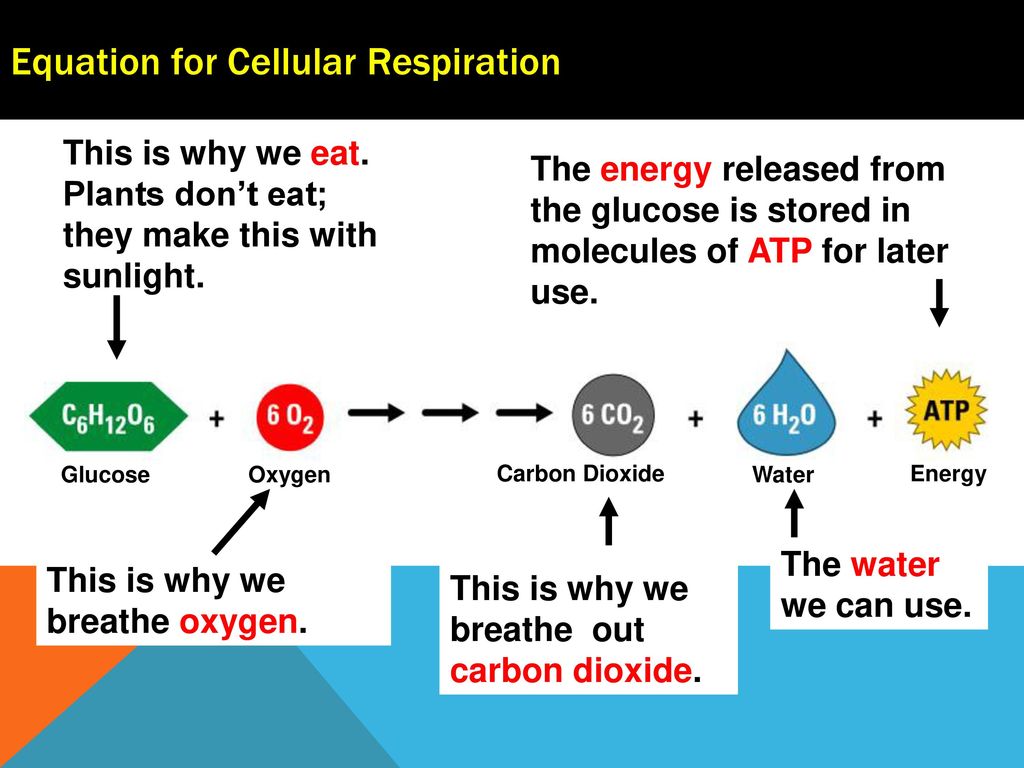
Cellular respiration in plants equation. Cellular Respiration Ck 12 Foundation. The second half of this equation is 6h2o 6co2 atp. The reaction for cellular respiration can be written in equation form as follows.
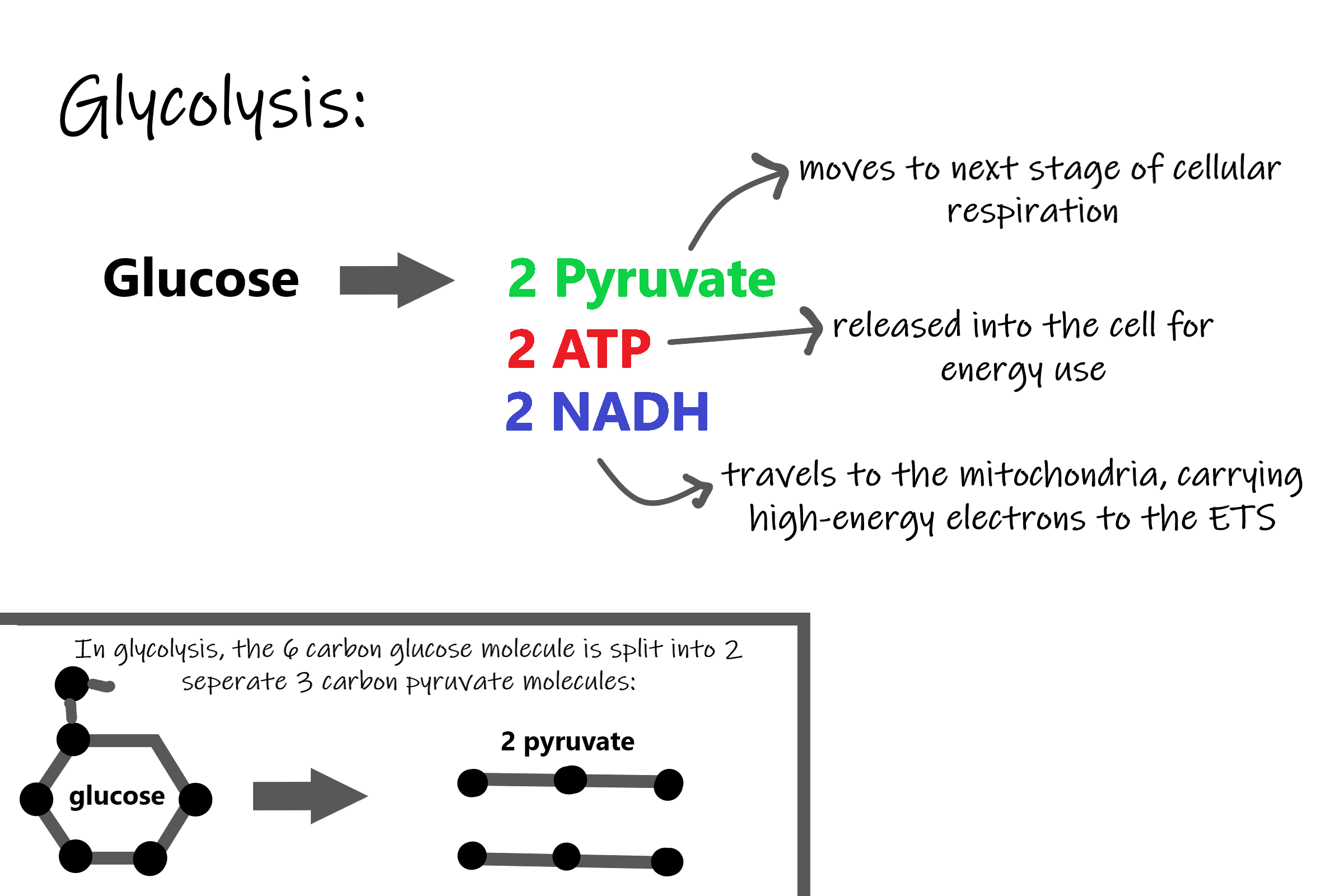
Glucose C 6 H 12 O 6 Oxygen O 2. Cellular respiration or aerobic respiration is a series of chemical reactions which begin with the reactants of sugar in the presence of oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water as waste products. L Glucose 4ADP 4Pi 2NAD 2Pyruvic acid 4ATP 2NADH l Two molecules of ATP were used up in the initial steps of glycolysis.
Cellular respiration involves many chemical reactions but they can all be summed up with this chemical equation. However cellular or aerobic respiration takes place in stages including glycolysis and the Krebs cycle. As this stage is aerobic it does need oxygen.
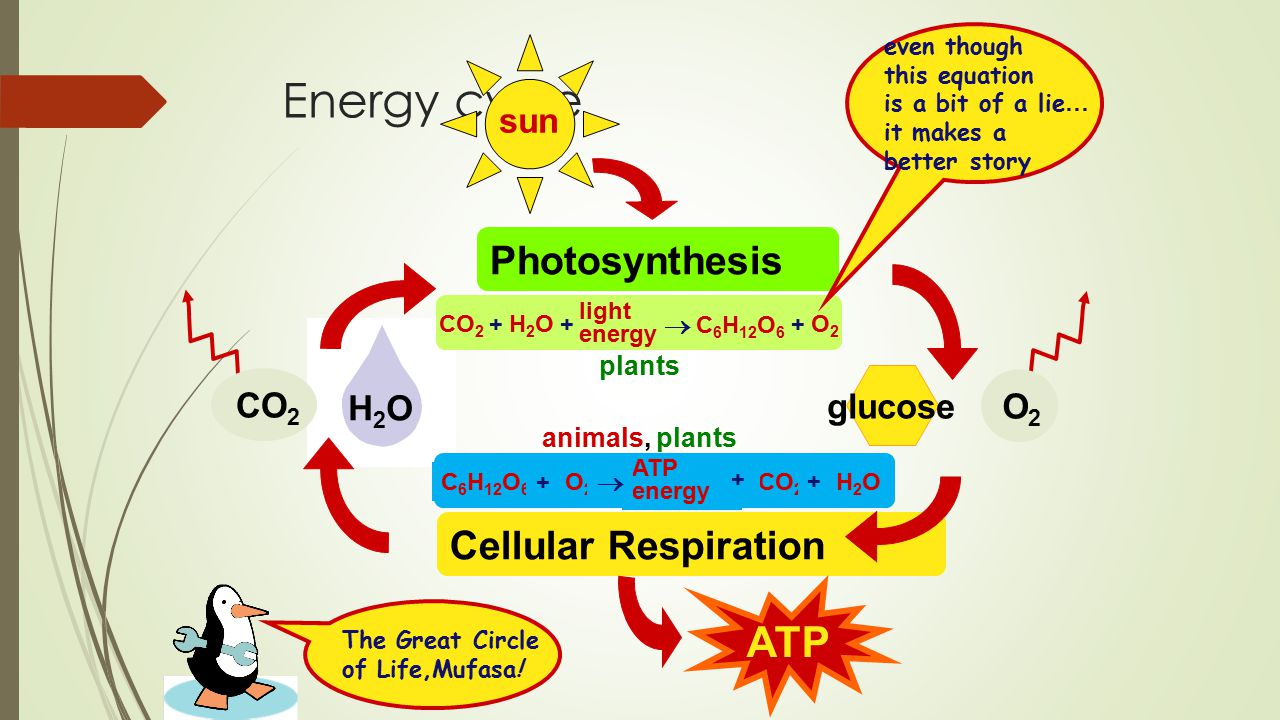
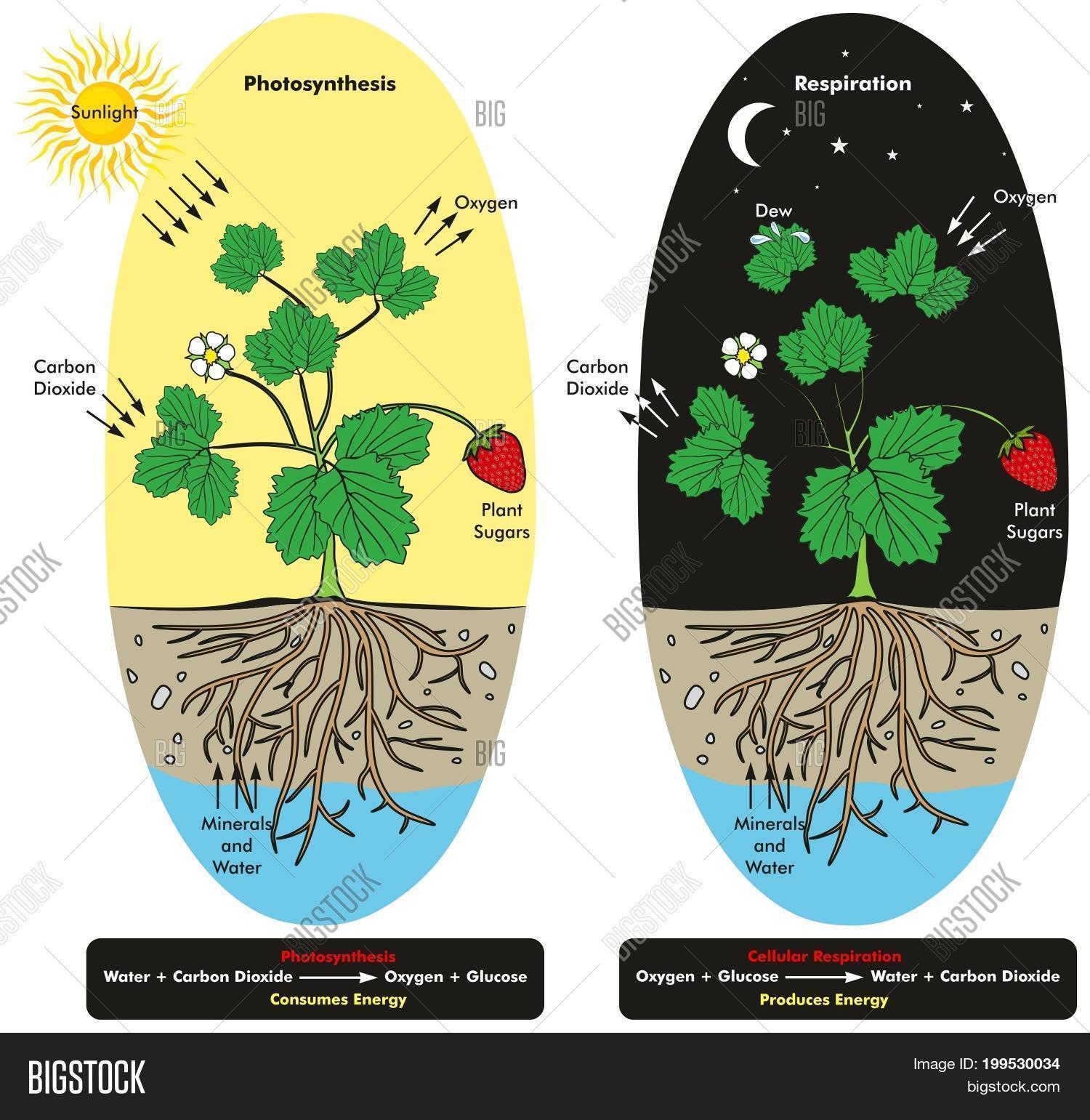
Thus the net gain of ATP during glycolysis is 4 2 2 ATP. It is an exergonic reaction where high-energy glucose molecules are broken down into carbon dioxide and water. Humans animals and plants depend on the cycle of cellular respiration and photosynthesis for survival.
Cellular Respiration In Plants Equation. This process occurs in the mitochondria the powerhouse of the cell. To emphasize this point even more the equation for photosynthesis is the opposite of cellular respiration.
Cellular respiration has the same chemical equation as photosynthesis. Photosynthesis Is An Anabolic Process Whereas. Here is the word equation for aerobic respiration.