Cell Membrane Structure And Function A Level

Different organelles have distinct structures and functions.
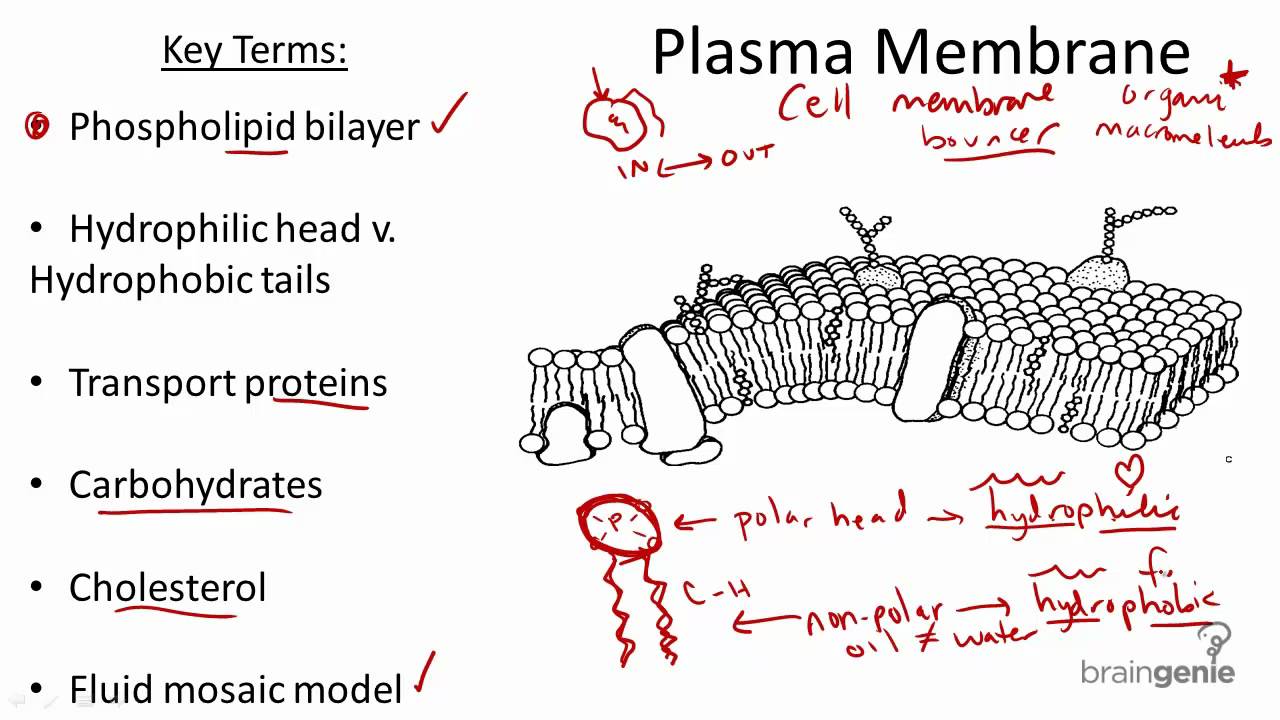
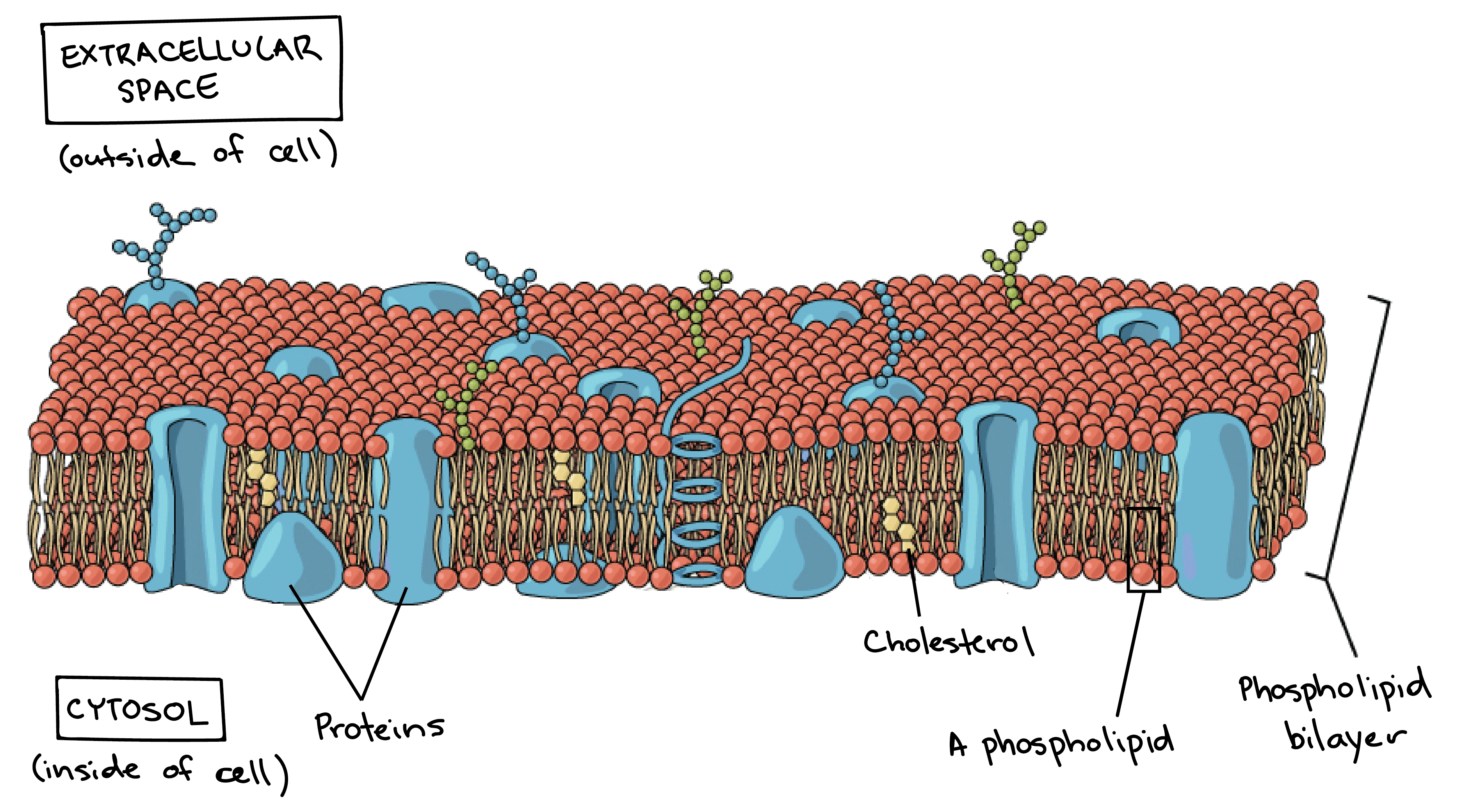
Cell membrane structure and function a level. Membranes formed from phospholipid bilayers help to compartmentalise different regions within the cell as well as forming the cell surface membrane Exam Tip An example of a membrane-bound organelle is the lysosome found in animal cells each containing many hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many different kinds of biomolecule. This is a thin flexible layer round the outside of all cells made of phospholipids and proteins. The Formation of Cell Membranes is Crucial to Life.
Scanning electron micrograph SEM of adipocytes Ad Membrane Structure and Function Prokaryotic Cells. The Nucleus is the largest organelle in a cell. Holds the cell content controls the insouts structural forms cell recognition adhesion signaling transport of substances endoexocytosis Cytoplasm.
Organisms are composed of cells and these cells have specific structures within in them that allow them to carry out their functions. Contains chromosomes DNA code for the synthesis of proteins that control the function of the cell hence the nucleus commands the cell Cell Surface membrane. Animal Cell Structure Nucleus.
These structures are called Organelles. Membrane Structure and Function Plasma Membrane. 1 Isolate cells contents from outside environment 2 Regulate exchange of substances between inside and outside of cell 3 Communicate with other cells Note.
Some of these proteins span the whole width of the membrane. Much of the membrane is made up of a sea of phospholipids with protein molecules floating in between the phospholipids. -A double membrane sac which pinches off the end of organelles such as the RER or Golgi Apparatus and fuses with other membranes such as the RER Golgi or Plasma Membrane Function of Vesicles -Transport proteins and other substances between organelles and the outside of the cell.
The liquid where all. Every cell has a lipid and protein layer called cell membrane or cytoplasmic or plasma which defines its boundaries and regulates molecular exchanges with the external environment. Membranes also exist within cells forming various.